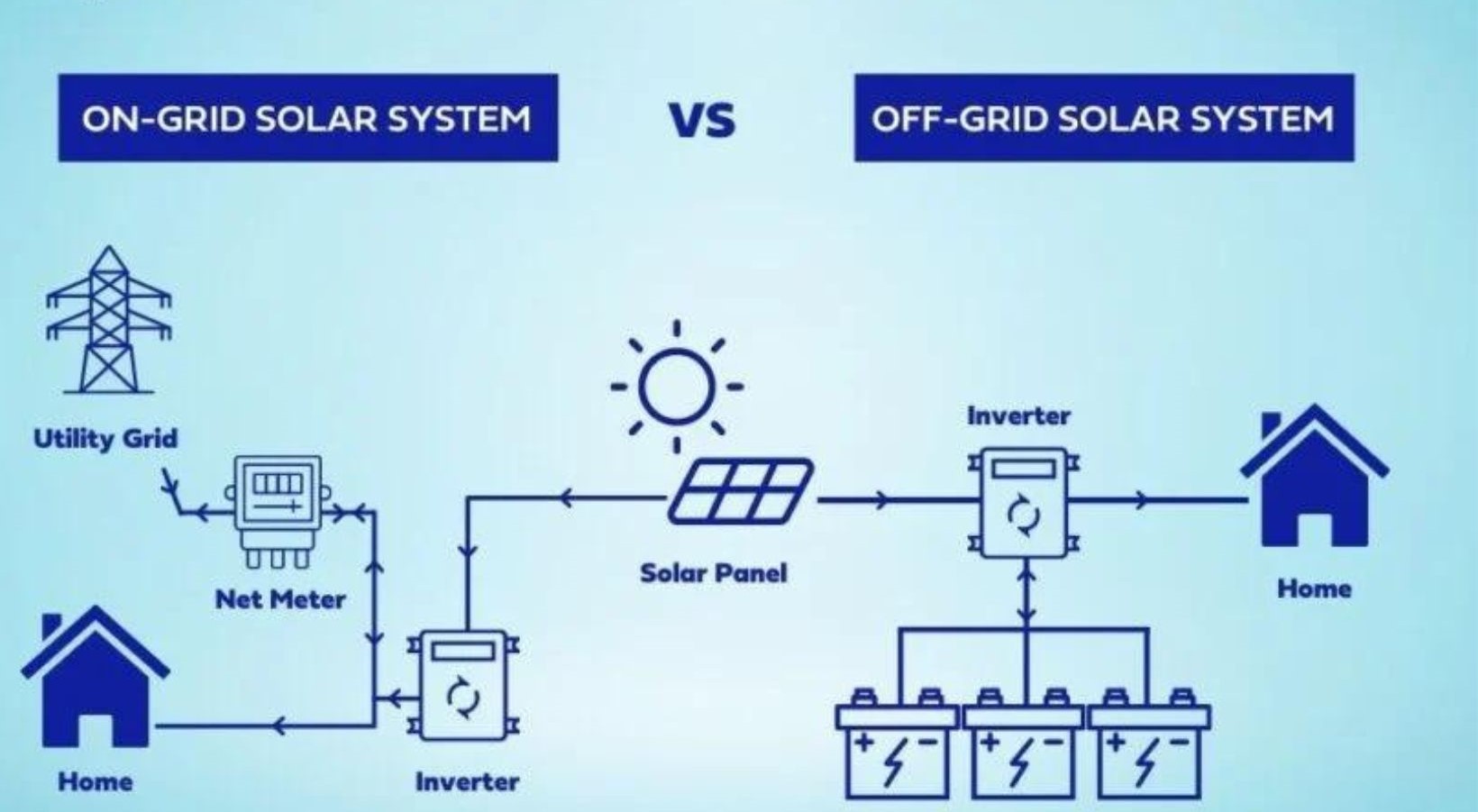
As the world intensifies its pursuit of sustainable and efficient power sources, solar energy has emerged as a central focus in this transformative journey. Among the myriad of solar solutions, two stand out prominently differences between on grid and off grid solar systems. In this insightful exploration, we embark on a detailed examination of the profound disparities characterizing these two approaches, aiming to illuminate the nuanced intricacies of their advantages, drawbacks, and essential considerations. By navigating through the intricate tapestry of on grid and off grid solar systems, we endeavor to provide a comprehensive understanding, allowing readers to navigate the complexities of these energy alternatives with clarity and informed decision-making
Introduction
Before embarking on a detailed exploration of the disparities between on grid and off grid solar systems, it’s imperative to establish a foundational understanding of the basic concepts underlying these approaches. On-grid solar systems intricately weave themselves into the existing power grid, creating a symbiotic relationship that facilitates the seamless exchange of electricity. This interconnectedness allows on-grid systems to draw power from the grid when needed and contribute surplus energy back to the grid, creating a dynamic and efficient energy flow.
On the contrary, the off-grid solar paradigm unfolds as a self-contained entity, operating independently of any external power infrastructure. In this self-sustained ecosystem, off-grid systems rely solely on the energy stored within their confines, typically in the form of advanced battery storage solutions. This fundamental distinction underscores the essence of these two solar systems, with on-grid systems embracing connectivity and exchange, while off-grid counterparts prioritize autonomy and self-sufficiency. This nuanced understanding lays the groundwork for a more profound exploration of the advantages, drawbacks, and considerations inherent in on grid and off grid solar system solutions.
Advantages of On-Grid Solar System
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary advantages of on-grid solar is its cost-effectiveness. The initial setup costs are often lower, thanks to the availability of grid infrastructure.
Grid Reliability
Being connected to the grid ensures a constant and reliable power supply, eliminating concerns about energy shortages.
Incentives and Subsidies
On-grid solar systems often qualify for government incentives and subsidies, making them financially appealing to many.
On Grid Net Metering
The concept of net metering in on-grid solar systems represents a game-changing approach to energy consumption and production. In simple terms, net metering allows individuals with on-grid solar installations to contribute excess electricity back to the grid. This surplus energy is not wasted; instead, it is measured and credited to the user’s account by the utility company. When energy needs surpass what the solar system generates, users can draw from these accumulated credits without incurring additional charges on their electricity bills.
Essentially, net metering transforms the traditional one-way flow of electricity into a dynamic, two-way interaction, enabling users to both consume and contribute electricity seamlessly. This not only promotes energy self-sufficiency but also serves as a powerful incentive for adopting on-grid solar systems, making them an environmentally conscious and economically viable choice for many.
Drawbacks of On-Grid Solar
Dependency on the Grid
However, the dependency on the grid can be a disadvantage during power outages or grid failures.
Lack of Energy Independence
Users of on-grid systems might face challenges during grid outages, compromising their energy independence.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar
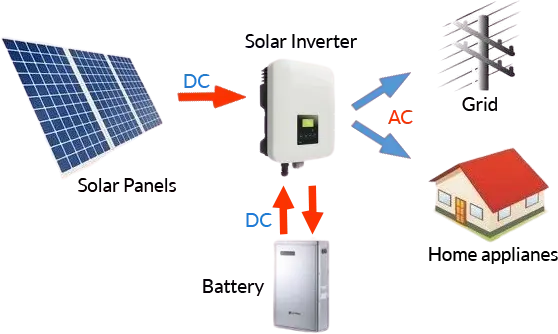
Energy Independence
Off-grid solar systems offer complete energy independence, ideal for locations with limited or no access to the grid.
Environmental Sustainability
These systems contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
Remote Location Suitability
Off-grid solar is perfect for remote locations where extending the power grid is impractical.
Drawbacks of Off-Grid Solar
Initial Setup Costs
The initial costs of setting up an off-grid system can be higher due to the need for energy storage solutions.
Limited Energy Production
Off-grid systems might face limitations in energy production, especially during extended periods of low sunlight.
Off Grid Net Metering
In an off-grid scenario, where solar systems operate independently without a connection to the main power grid, net metering is not applicable. Off-grid systems rely on energy storage solutions, typically batteries, to store excess energy for later use during periods of low sunlight. Since there is no grid connection for off-grid systems, the compensatory mechanism of net metering, where surplus energy is fed back into the grid for credits, is unavailable. This limitation can impact the overall efficiency and financial incentives associated with off-grid solar systems, making it essential for users to carefully weigh the pros and cons based on their specific energy needs and circumstances
Key Differences Between On Grid and Off Grid Solar system
Connection to the Grid
The fundamental difference lies in whether the system is connected to the main power grid or operates independently.
Battery Storage
Off-grid systems require robust battery storage solutions to store excess energy for later use, a feature not necessary for on-grid systems.
Reliability
On-grid systems offer reliability through continuous access to the grid, while off-grid systems rely on stored energy, which may be limited.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Considering residential, commercial, or industrial applications is crucial when deciding between on grid and off grid solar system solutions.

Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Comparing the carbon footprint and impact on the power grid helps in understanding the overall environmental implications
Cost Analysis
Evaluating initial costs and long-term savings provides a comprehensive perspective on the financial aspects of each system.
Maintenance Requirements
Understanding the maintenance requirements of on grid and off grid solar systems is essential for long-term efficiency
Technological Advancements
Exploring the latest innovations in on grid and off grid solar system technologies showcases the industry’s ongoing evolution.
Case Studies
Real-world examples highlight successful installations and the practicality of on grid and off grid solar system solutions
Conclusion
n summary, the choice between on grid and off grid solar system depends on specific needs and priorities. Understanding the differences outlined here can guide individuals and businesses toward making informed decisions that align with their energy goals
FAQs
Are on-grid solar systems more cost-effective in the long run?
The long-term cost-effectiveness depends on factors such as energy consumption, incentives, and grid reliability.
How do off-grid solar systems handle power outages?
Off-grid systems rely on stored energy in batteries, providing a continuous power supply during outages.
Can on-grid solar systems operate independently during grid failures?
No, on-grid systems are dependent on the grid and may not function independently during power outages.
What advancements can we expect in on grid and off grid solar system technologies?
Ongoing innovations include improvements in energy storage, efficiency, and grid integration.
Is the environmental impact of on grid solar system significantly lower than off grid solar system
Off-grid systems generally have a lower environmental impact, as they reduce reliance on conventional power sources.